Why these differences are important for C> development
Despite the long-standing similarities in traditional drug categories like small molecules, the US FDA and the EU EMA have yet to align their guidance on emerging therapies. This includes Cell and Gene Therapies (CGTs) and their EU equivalent, Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs).
Given the differences in product categorization, it’s crucial for sponsors to understand regional variations early in the development process. By seeking regulatory guidance and utilising additional communication opportunities for CGTs/ATMPs in each jurisdiction, much of the uncertainty surrounding the development of these innovative therapies can be alleviated. This is particularly important as development timelines in this regulatory space can be accelerated.
Understanding the unique classifications and manufacturing guidelines in each region can greatly assist in the accurate documentation of details, which is essential for a successful market application in each jurisdiction.
1. Terminology: CGT vs. ATMP
The first major difference between US and EU regulatory processes is the terminology.
In the US, Cell and Gene Therapies (CGTs) are seen as biologics. This group includes human gene therapy products, cell therapy products, and human cells, tissues, and cellular and tissue-based products (HCT/Ps). It’s important to note that HCT/Ps have their own separate regulations.
In contrast, in the EU, all these products are grouped together as Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs). ATMPs are then split into gene therapy, cell therapy, and tissue-engineered categories. The different names for CGTs and ATMPs can affect how a product is classified in each jurisdiction.
Sponsors need to work out which category their products fit into to make sure they’re following the right steps for review and approval.
2. Guidance documents and governing regulations
Understanding the key laws and definitions that oversee the development, handling, and production of specialised biologics is the initial step towards compliance and successful process planning.
Making use of guidance documents and statements issued by each agency can simplify the process significantly.
Summary of jurisdiction-specific regulations and recent guidance documents: US vs EU

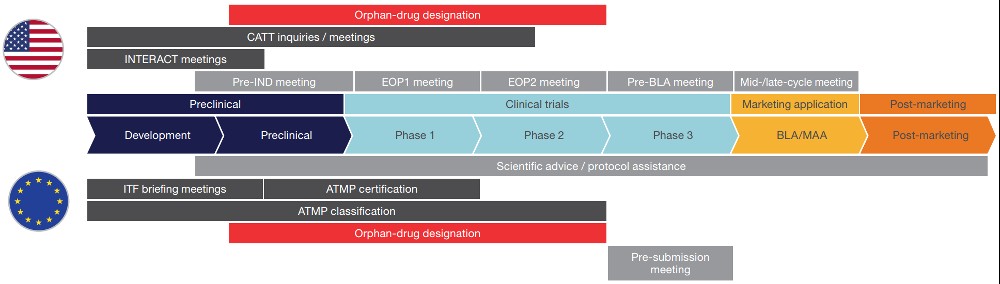
3. Regulatory Interaction and Approval Pathways
Given the unique nature and inherent uncertainty in introducing new CGTs to the market, both developers and regulatory agencies have additional opportunities for interaction throughout the development process in both the US and EU.
Eligibility for these meetings varies depending on the type of product. There are also extra opportunities to qualify for special designations and review programmes that can increase accessibility to regulators and potentially speed up review timelines.
In the US, such programmes include priority review, accelerated approval, fast-track status, breakthrough therapy designation, and regenerative medicine advanced therapy classifications.
In the EU, the criteria for designation as an orphan drug are stricter, and accelerated assessment, conditional approval, and the Priority Medicines programme (PRIME) are available as special programme options, depending on the drug criteria.
Generally, these meeting opportunities allow for earlier and more frequent communication with regulators than is typically possible for other developers. These opportunities are more heavily weighted towards early interactions, but sponsors can engage with regulators throughout the entire process.
Regulatory advice opportunities by phase of development
Dark grey indicates meetings only available for CGT/ATMP developers
4. Manufacturing Expectations
Due to the possibility of expedited review, the timelines for Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) development are often shortened for CGTs/ATMPs. Despite this, there are many similarities in the manufacturing requirements of the US and EU.
However, significant differences in product classification can greatly change inspection processes and documentation expectations. For instance, in the US, viral vectors are considered a biologic drug substance. This typically means that facilities must be licensed and inspected for quality metrics related to vector purity, potency, safety, and handling.
In contrast, in the EU, viral vectors can sometimes be classified as starting materials, especially if used in a cell therapy or as an ex vivo gene therapy based on genetically modified cells. They may not always be subject to the same level of oversight as drug substances, but good manufacturing practices are often still required.
Despite these technicalities, the primary goal of each region’s regulations is to protect patient health and safety. By understanding which elements of the drug product are critical, and by demonstrating their purity, origin, and quality, developers should have enough data to satisfy either agency. An experienced Contract Development and Manufacturing Organisation (CDMO) can help manage differing expectations by product type.
5. Commercialisation Requirements
Shorter approval timelines, due to specific filing pathways or special categorisations like orphan drugs, can pose a challenge for CGT/ATMP development. Sometimes, submission readiness arrives quicker than expected, requiring developers to make swift decisions about scale-up, assays, and validation considerations. In other instances, the small batch sizes needed due to starter material availability can make ongoing production uncertain; changes in supply sources or quality necessitate repeated validation, which can quickly become costly and problematic.
Planning a global submission strategy, choosing a competent manufacturing site, and selecting suitable validation assays and an overall validation strategy early in development can ease the transition to commercialisation and support companies through variations in jurisdictional requirements for quality testing and manufacturing for distribution.
By understanding regional guidance and legislation related to commercial products before market approval, developers can plan for commercialisation requirements earlier.
With proactive, effective scaling plans, thoughtful selection of manufacturing processes, and an experienced site, the challenges associated with commercialisation (even with differing requirements by country) can be significantly reduced.
Site selection considerations
Choosing the right site can help you reach your regulatory milestones faster, reduce regulatory risk, and build for commercial success.
With fewer than 90 CDMOs managing viral vector-associated products worldwide, selecting a site with experience and verified, appropriate licensing can make a significant difference to commercialisation success.
Additional considerations for commercial production site selection include:
- Experienced leadership team with a strong track record
- Scale and capacity flexibility
- Tech transfer and manufacturing success rate
- Robust materials management
- Facility design features for viral vector manufacturing
- Effective cleaning and cross-contamination controls in place
- Proven regulatory and compliance track record
As more data accumulate from a growing number of CGT/ATMP approvals, it is expected that regulators will gain a better understanding of how safety, purity, and potency affect patients, either in the clinic or in the market. Over time, regulators may converge on harmonised expectations.
While sponsors await more formal guidance from each jurisdiction, they can use numerous tools to minimise the confusion and delay caused by the differences in terminology and regulations between the FDA and EMA.
From early consultation with research and CDMO partners to proactive selection of multiple assays and qualified production sites, sponsors can lay the groundwork for effective processes and approaches to minimise regulatory challenges and maximise their chances of market approval in both jurisdictions.
About Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Fisher Scientific provides industry-leading pharma services solutions for drug development, clinical trial logistics and commercial manufacturing to customers through our Patheon brand. With more than 65 locations around the world, we provide integrated, end-to-end capabilities across all phases of development, including API, biologics, viral vectors, cGMP plasmids, formulation, clinical trials solutions, logistics services and commercial manufacturing and packaging.
Built on a reputation for scientific and technical excellence, we provide pharma and biotech companies of all sizes instant access to a global network of facilities and experts across the Americas, Europe, Asia and Australia. We offer integrated drug development and clinical services tailored to fit your drug development journey through our Quick to Care™ program. Our Quick to Clinic™ programs for large and small molecules help you balance speed and risk during early development so you can file your IND quickly and successfully. Digital innovations such as our mysupply Platform and Pharma 4.0 enablement offer real-time data and a streamlined experience. Together with our customers, we’re rapidly turning pharmaceutical possibilities into realities.
 Stay ahead of trends and best practices
Stay ahead of trends and best practices
 Exclusive downloads and podcasts
Exclusive downloads and podcasts
 Get invites to special events and meetups
Get invites to special events and meetups  Stay ahead of trends and best practices
Stay ahead of trends and best practices
 Exclusive downloads and podcasts
Exclusive downloads and podcasts
 Get invites to special events and meetups
Get invites to special events and meetups