In the biopharmaceutical industry, small molecule contract manufacturing plays a critical role in bringing new therapies to market.
Small molecule drugs, characterised by their low molecular weight, are essential in treating a wide range of diseases due to their ability to interact precisely with biological targets. Selecting the right CDMO partner can significantly impact the success of a pharmaceutical company’s drug development pipeline.
This article explores the key aspects of small molecule contract manufacturing, the services provided by CDMOs, market size, and industry trends.
What is a Small Molecule in Pharma?
A small molecule in the pharmaceutical industry refers to a low molecular weight organic compound, typically less than 900 daltons. These compounds are designed to interact with biological molecules within the body to mimic, enhance, or inhibit their natural functions. They are generally stable, easily customisable, and can be administered in various forms, such as pills, inhalers, or injectables. Their predictable behaviour in the body allows for straightforward dosing protocols, making them suitable for a wide range of therapeutic applications.
Small Molecule Contract Manufacturing:
Small molecule contract manufacturing refers to the outsourcing of the production of small-molecule drugs to specialised organisations. These organisations, known as Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), offer a range of services from early-stage development to commercial-scale production.
Sub-Categories:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Manufacturing: Focuses on producing the active components of the drug.
- Drug Product Manufacturing: Involves formulating APIs into final dosage forms like tablets, capsules, and injectables.
- Clinical Trial Material (CTM) Manufacturing: Provides manufacturing services specifically for clinical trials.
- Analytical and Stability Testing: Offers analytical services to ensure drug quality and stability over time.
How big is the small molecule CDMO market?
The global small molecule CDMO market was valued at USD 71.3 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 126.2 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 6.7% from 2025 to 2033. This expansion is driven by increasing strategic outsourcing, strong drug development pipelines, and evolving global manufacturing dynamics. (Source- Grandview Research)
The significance of small molecules in expanding global therapeutic innovations remains pronounced. Specialty medicines are significantly steering pharmaceutical industry growth globally, where small molecule applications contribute to more than half of specialty sales.
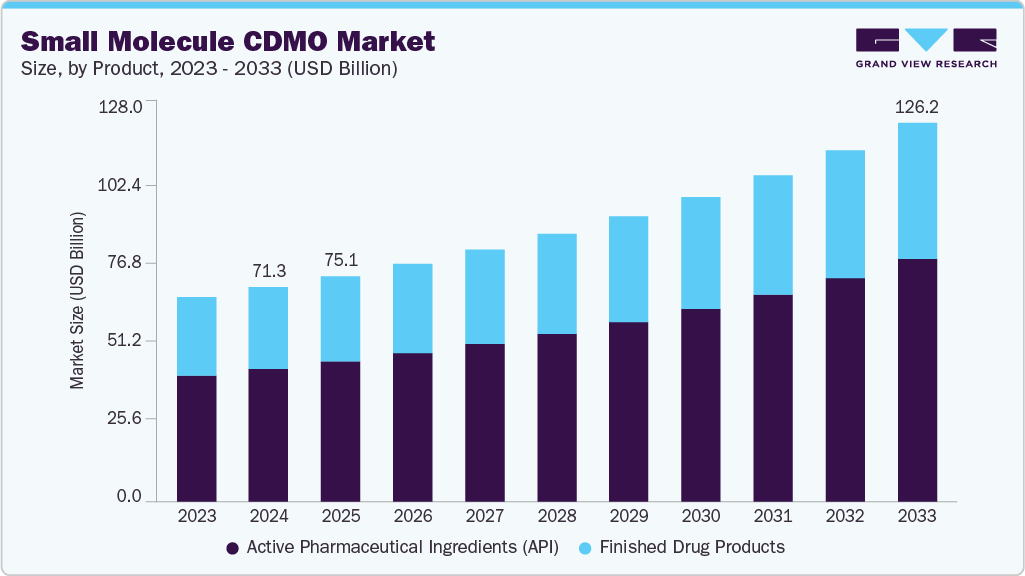
The small molecule CDMO market in the U.S. held the largest share in 2024. This is attributed to the increasing number of clinical trials in the U.S. For instance, according to the National Clinical Trials Registry (NCT), around 12,326 clinical trials studies were underway across various phases for the treatment of cancer in 2022. (Source- Grandview Research)
There are a high number of Small Molecule contract development and manufacturing organisations. This infographic summarises the largest (those small molecule API manufacturers with 2 facilities or more) operating in Europe.
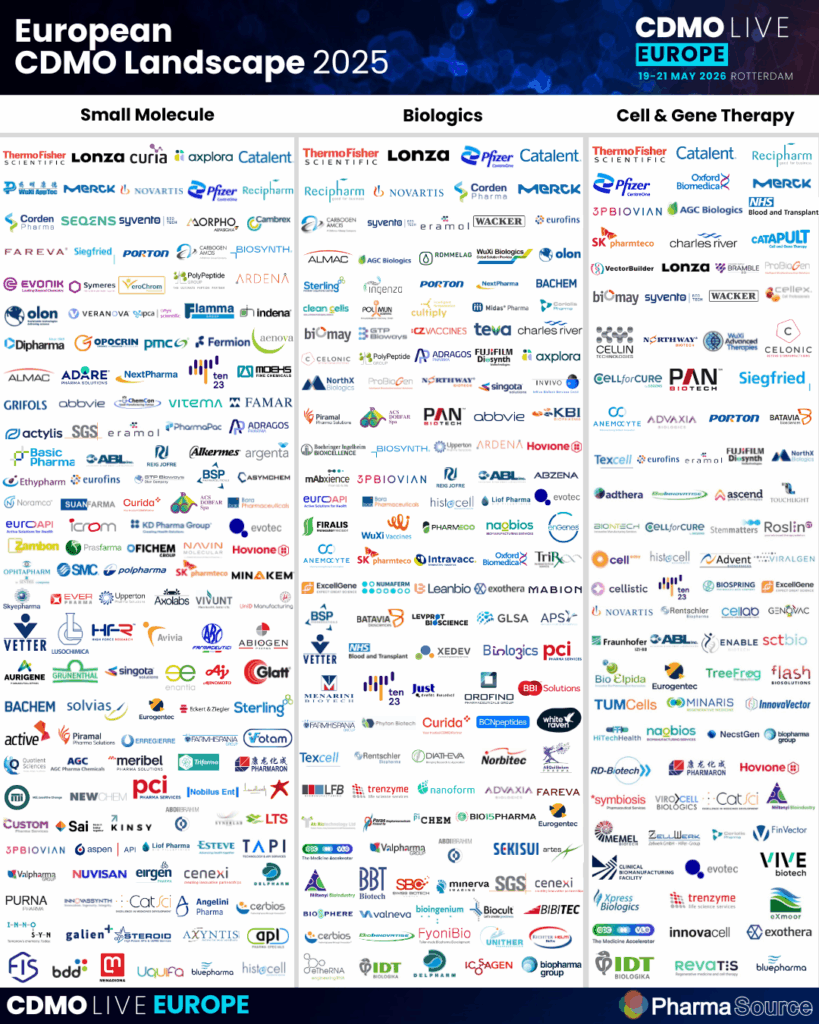
- Download the European CDMO infographic here and the North American CDMO infographic here
Key trends in small molecule contract manufacturing
The small molecule contract manufacturing landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing market demands, and stringent regulatory requirements.
Here are the key trends that are shaping the industry
1. Adoption of Advanced Technologies
The use of advanced technologies like continuous manufacturing, process analytical technology (PAT), and automation is transforming small molecule contract manufacturing.
Continuous manufacturing enhances efficiency and consistency, while PAT allows for real-time monitoring and quality control. Automation and digitalisation streamline operations, reduce human error, and boost productivity, leading to higher quality products and faster time-to-market.
2. Focus on Green Chemistry and Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a critical focus in small molecule manufacturing. Companies are adopting eco-friendly manufacturing processes, energy-efficient technologies, and waste reduction strategies. These practices not only reduce environmental impact but also align with regulatory requirements and improve cost-effectiveness. Emphasising green chemistry helps companies meet growing consumer and regulatory demands for sustainable products.
3. Increased Outsourcing and Strategic Partnerships
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly outsourcing manufacturing to focus on core competencies like R&D and marketing. This trend has led to the globalisation of supply chains and the formation of strategic alliances. By partnering with specialised CMOs, companies can access advanced technologies, streamline their operations, and accelerate time-to-market, ultimately enhancing innovation and efficiency.
4. Regulatory and Quality Compliance
The regulatory landscape is becoming more stringent, necessitating robust quality management systems and a focus on data integrity. CMOs are implementing comprehensive quality assurance processes to ensure compliance with global standards such as GMP, FDA, and EMA guidelines. This focus on regulatory and quality compliance ensures the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products, reducing the risk of regulatory setbacks.
5. Innovation in Drug Delivery and Formulation
Innovation in drug delivery and formulation is a significant trend in small molecule contract manufacturing. Advanced drug delivery systems, complex formulations, and personalised medicine are becoming more prevalent. These innovations improve drug efficacy, patient compliance, and therapeutic outcomes. CMOs are increasingly developing nanoformulations, fixed-dose combinations, and customised therapies to meet the growing demand for specialised treatments.
Technological Advancements
The small molecule CDMO market is rapidly evolving as companies adopt technologies that enable faster, safer, and more cost-efficient drug development. CDMOs are increasingly implementing continuous manufacturing, flow chemistry, and process intensification to enhance scalability and reduce waste, while meeting rising regulatory expectations. Automation, digital process control, PAT, and real-time release testing (RTRT) are improving batch consistency and minimizing manual intervention.
Advanced data analytics, AI-driven modeling, and digital twins are optimizing process parameters, predicting yield variations, and accelerating tech transfer. Growing demand for sustainable production is also driving investment in green chemistry, including solvent recycling and bio-catalysis. Collectively, these advancements enable shorter time-to-market and position CDMOs as strategic innovation partners for complex APIs, personalized medicines, and fast-track therapeutics.
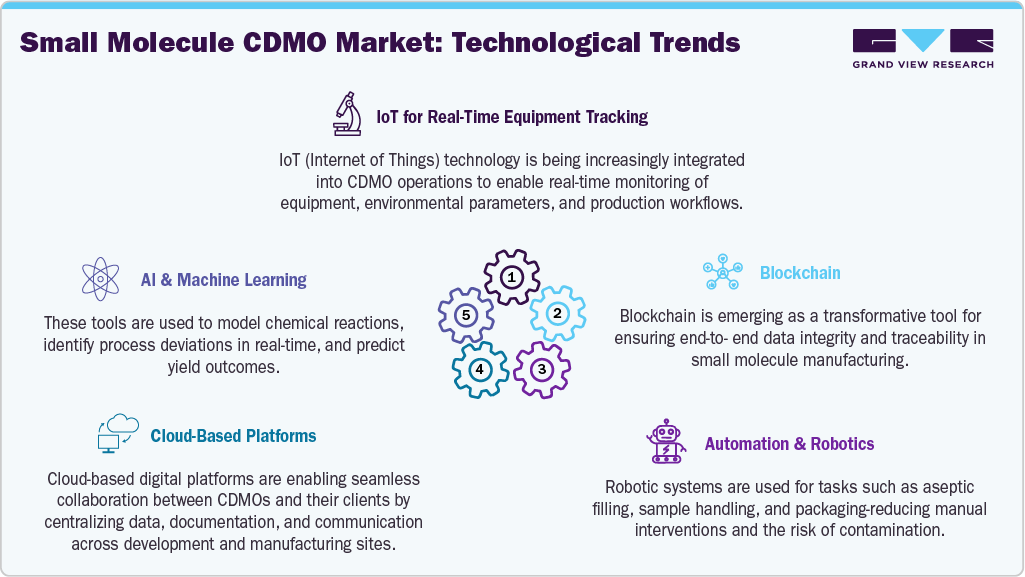
Source- Grandview Research
What are the services to expect from Small Molecule CDMO?
Small Molecule Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) provide a comprehensive range of services to support the development and production of small molecule drugs. Here are the key services you can expect from a Small Molecule CDMO:
1. Drug Discovery and Development
- Lead Identification and Optimization: Screening and optimizing potential drug candidates to improve efficacy, selectivity, and safety.
- Preformulation Studies: Assessing the physical and chemical properties of the drug candidate to guide formulation development.
- Formulation Development: Creating suitable drug formulations for various delivery methods (e.g., oral, injectable).
2. Process Development
- Route Scouting and Development: Identifying and developing efficient synthetic routes for drug production.
- Process Optimization: Enhancing the manufacturing process to maximise yield, purity, and cost-efficiency.
- Scale-Up: Transitioning from laboratory-scale synthesis to larger batch production suitable for clinical trials and commercial manufacturing.
3. Analytical Development
- Analytical Method Development: Developing and validating analytical methods to ensure the quality, potency, and purity of the drug.
- Stability Testing: Conducting studies to determine the shelf-life and storage conditions of the drug.
- Quality Control: Implementing rigorous testing protocols to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
4. Clinical Trial Manufacturing
- GMP Manufacturing: Producing clinical trial materials under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) conditions.
- Packaging and Labelling: Preparing clinical trial materials with appropriate packaging and labelling for patient use.
- Supply Chain Management: Coordinating the logistics of clinical trial material distribution.
5. Commercial Manufacturing
- Large-Scale Production: Manufacturing drug products at commercial scale, ensuring consistency and quality.
- Packaging and Serialization: Providing final packaging solutions, including serialisation to meet regulatory requirements.
- Quality Assurance and Control: Ensuring all manufacturing processes meet stringent quality standards and regulatory requirements.
6. Regulatory Support
- Regulatory Submissions: Assisting with the preparation and submission of regulatory documents to agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and others.
- Compliance Consulting: Providing guidance on regulatory compliance throughout the drug development and manufacturing process.
7. Specialized Services
- High Potency Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (HPAPIs): Handling and manufacturing of highly potent compounds with specialised containment facilities.
- Solid State Chemistry: Offering services such as polymorphism screening, salt selection, and crystallisation process development.
- Micronization and Particle Size Control: Providing techniques to control the particle size for improved drug delivery and bioavailability.
8. Post-Marketing Support
- Lifecycle Management: Supporting the ongoing production and optimization of commercial products.
- Process Improvement: Continuously improving manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Product Enhancements: Developing new formulations or delivery methods to extend the product lifecycle.
9. Technical Transfer
- Technology Transfer: Transferring processes and technologies from development to manufacturing, ensuring a smooth scale-up.
- Knowledge Management: Maintaining comprehensive documentation and knowledge transfer to support continuous improvement.
Differences between CMO, CRO, and CDMOs
The pharmaceutical industry relies on various external partners to streamline drug development and manufacturing processes, with key partners including Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs).
Understanding the differences between these entities is crucial for biopharmaceutical companies in selecting the right partner for their needs, and depends largely on the phase of their drug in the pipeline from early-phase discovery to commercial manufacturing.
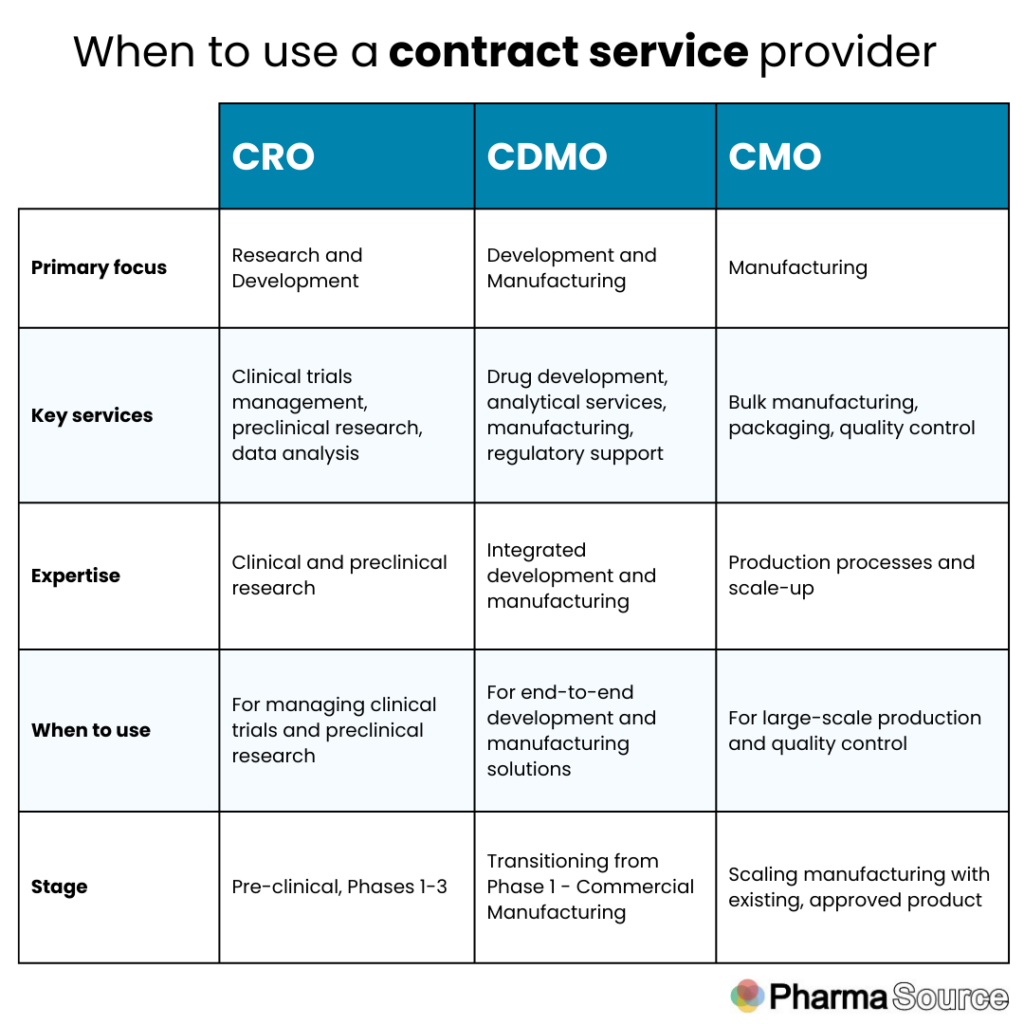
1. Contract Manufacturing Organisation (CMO)
Definition: A Contract Manufacturing Organization (CMO) provides manufacturing services to pharmaceutical companies. CMOs focus on the production aspect, offering expertise in manufacturing processes, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
Key Services:
- Bulk Manufacturing: Large-scale production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished dosage forms (tablets, capsules, injectables, etc.).
- Packaging and Labelling: Secondary services such as packaging, labelling, and ensuring products meet regulatory standards.
- Quality Control and Assurance: Ensuring the manufactured products meet quality and regulatory standards through rigorous testing and validation processes.
- Scale-Up: Transitioning from small-scale production to large-scale manufacturing as a drug moves through clinical trials to commercialization.
When to Use a CMO:
- When a pharmaceutical company needs to scale up production.
- When in-house manufacturing capabilities are lacking or insufficient.
- For cost-effective and time-efficient production solutions.
Example: A pharmaceutical company with an approved drug may outsource its production to a CMO to ensure high-quality, large-scale manufacturing.
2. Contract Research Organization (CRO)
Definition: A Contract Research Organization (CRO) provides outsourced research services to pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies. CROs primarily focus on the early stages of drug development, including preclinical and clinical research.
Key Services:
- Clinical Trials Management: Designing, managing, and conducting clinical trials (Phases I-IV).
- Preclinical Research: Conducting laboratory and animal studies to assess the safety and efficacy of drug candidates before clinical trials.
- Regulatory Affairs: Assisting with regulatory submissions and ensuring compliance with global regulatory standards.
- Data Management and Analysis: Collecting, managing, and analysing clinical trial data to support regulatory submissions and decision-making.
- Biostatistics: Providing statistical analysis to interpret trial results and ensure robust data.
When to Use a CRO:
- When a pharmaceutical company lacks the resources or expertise to conduct clinical trials.
- For managing complex, multi-site clinical trials.
- To accelerate the drug development timeline through specialised expertise.
Example: A biotech company with a promising drug candidate may partner with a CRO to manage the clinical trials needed to obtain regulatory approval.
3. Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO)
Definition: A Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) combines the services of both CMOs and CROs, offering comprehensive development and manufacturing solutions. CDMOs provide end-to-end services from drug development through to commercial manufacturing.
Key Services:
- Drug Development: Formulation development, process development, and analytical method development.
- Manufacturing: Both clinical trial materials and commercial-scale production, including bulk manufacturing and packaging.
- Regulatory Support: Assistance with regulatory filings, compliance, and audits.
- Supply Chain Management: Integrated logistics, warehousing, and distribution services.
- Scale-Up and Technology Transfer: Transitioning from development to large-scale production, including technology transfer and validation.
When to Use a CDMO:
- For seamless transition from drug development to manufacturing.
- When a pharmaceutical company seeks to streamline the supply chain and reduce time-to-market.
- For integrated solutions that combine development and manufacturing expertise.
Example: A pharmaceutical company with a new drug candidate might engage a CDMO to handle formulation development, scale-up, and eventual large-scale production, ensuring a smooth transition through the various stages of drug development and manufacturing.
Tune into the PharmaSource podcast, where Elisabeth Stampa (Medicines for Europe), Elena Barboni (Flamma), and Agneta Larhed (RegSmart Life Science) explore how European small molecule manufacturing is at a critical turning point as emerging green regulations intersect with market realities.
How to choose the right small molecule CDMO for you?
Choosing the right Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) for small molecule production can make or break your pharmaceutical project. It’s a crucial decision that demands careful consideration. Here’s an engaging and detailed guide to help you navigate this critical choice:
1. Understand Your Needs and Goals
Before you start your search, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your specific needs and goals. Ask yourself:
- What stage is your project at? (Development, clinical trials, commercial production)
- What are your production scale requirements?
- What specific services do you need? (Formulation development, analytical testing, manufacturing)
- What are your timelines and budget constraints?
2. Look for Industry Experience and Expertise
Not all CDMOs are created equal. You want a partner with a proven track record in small molecule development and manufacturing. Look for:
- Experience: How long has the CDMO been in business? Do they have experience with similar projects?
- Expertise: Do they specialise in small molecules? What technologies and processes do they use?
- Case Studies and Testimonials: Look for success stories and references from previous clients.
3. Evaluate Technical Capabilities
Your chosen CDMO should have state-of-the-art facilities and technical capabilities to handle your project. Key considerations include:
- Facilities: Do they have modern, well-maintained facilities? Are they equipped to handle your specific needs (e.g., high-potency APIs, complex formulations)?
- Technology: Are they using the latest technologies for continuous manufacturing, process analytical technology (PAT), and automation?
- Scalability: Can they scale up production as your project progresses?
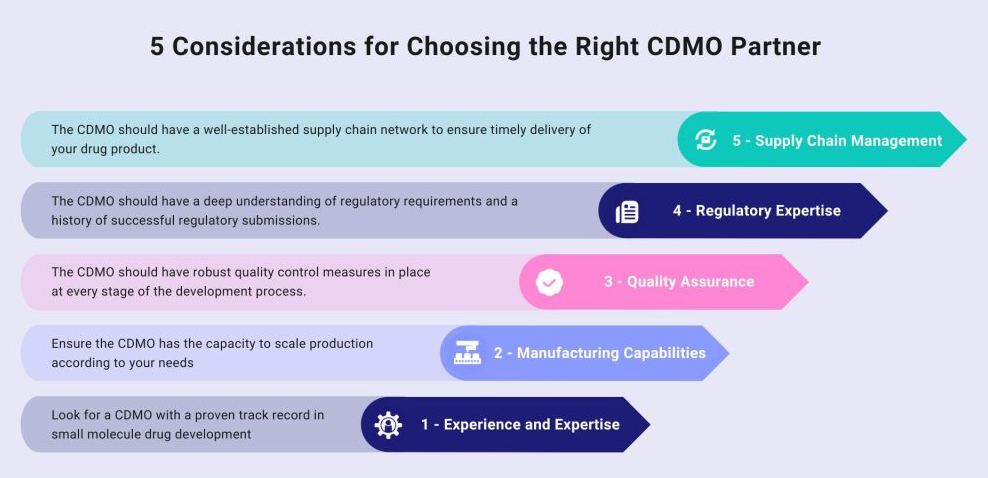
4. Assess Regulatory Compliance and Quality Standards
Regulatory compliance and quality are non-negotiable in the pharmaceutical industry. Ensure the CDMO adheres to the highest standards by checking:
- Certifications: Do they comply with GMP, FDA, EMA, and other relevant regulations?
- Quality Management Systems: Do they have robust quality control and assurance processes in place?
- Audit History: Have they passed recent regulatory audits and inspections?
5. Consider Financial Stability
Partnering with a financially stable CDMO is crucial to avoid disruptions. Assess their financial health by:
- Financial Reports: Review their financial statements and annual reports.
- Reputation: Check their reputation in the industry. Are they known for reliability and stability?
- Partnerships: Are they backed by strong partnerships or parent companies?
6. Evaluate Their Communication and Project Management Skills
Effective communication and project management are vital for a successful partnership. Look for:
- Communication: Are they responsive and transparent? Do they provide regular updates?
- Project Management: Do they have dedicated project managers? What project management tools and methodologies do they use?
- Problem-Solving: How do they handle issues and challenges? Are they proactive and solution-oriented?
7. Inspect Their Supply Chain and Logistics Capabilities
A robust supply chain and logistics network can significantly impact your project’s success. Evaluate their capabilities by:
- Supply Chain: Do they have reliable suppliers for raw materials and components? How do they manage supply chain risks?
- Logistics: Are they efficient in handling shipping, storage, and distribution? Do they offer global logistics support?
- Sustainability: Are they committed to sustainable practices in their supply chain?
8. Request a Site Visit
Seeing is believing. Arrange a site visit to get a firsthand look at their facilities, meet their team, and assess their operations. During the visit:
- Facilities Tour: Inspect their manufacturing plants, labs, and quality control areas.
- Team Interaction: Meet with key personnel, including project managers, quality control experts, and technical staff.
- Process Review: Observe their processes and workflows. Are they efficient and well-organized?
9. Prepare a Comprehensive RFP
Once you’ve shortlisted potential CDMOs, prepare a detailed Request for Proposal (RFP). Include:
- Project Overview: Describe your project, including timelines, deliverables, and specific requirements.
- Technical Specifications: Detail the technical aspects, such as formulation, scale, and analytical methods.
- Evaluation Criteria: Outline how you will assess the proposals, including key performance indicators and benchmarks.
- Questions: Include specific questions to assess their capabilities, experience, and approach.
10. Compare Proposals and Make an Informed Decision
Carefully review and compare the proposals based on your evaluation criteria. Consider:
- Technical Fit: Does the CDMO have the technical capabilities and expertise to meet your needs?
- Cost: Are their pricing and payment terms transparent and competitive?
- Cultural Fit: Do they share your values and approach to quality, innovation, and customer service?
- References: Follow up on references and case studies to validate their claims.
Choosing the right small molecule CDMO is a pivotal decision that requires thorough research and careful evaluation. By understanding your needs, assessing potential partners’ capabilities and experience, and conducting a detailed comparison, you can select a CDMO that aligns with your goals and sets your project up for success.
Prof Tom Moody, VP API Development and Commercialisation, Almac Sciences shares- Best Practices for Sponsors to Maximize CDMO Partnerships

Sponsors can get the most from CDMO collaborations by focusing on clear processes, quality-driven partner selection, and strategic integration. Defining technical processes upfront prevents delays during tech transfer, scale-up, and regulatory inspections. Choosing CDMOs with strong commercial stability, regulatory compliance, and continuous investment ensures long-term reliability.
Leveraging a CDMO’s integrated expertise—advanced technologies, vertical integration, and multidisciplinary teams—reduces the need for internal resources and accelerates API development. Strong governance frameworks, including joint steering committees and ICH/FDA-aligned quality agreements, enable proactive risk management while maintaining collaboration efficiency.
Integrating drug substance and drug product development under one CDMO further streamlines timelines, improves communication, and reduces operational risk. In a competitive market, sponsors who prioritise transparency, rigorous evaluation, and effective governance unlock the full potential of CDMO partnerships.
For the latest information about this fast-moving sector, make sure you join us at CDMO Live.
The Future of Small Molecule Drugs
Despite the growing focus on biologics, small molecule drugs remain essential to modern therapeutics. Their versatility, cost-efficient manufacturing, oral bioavailability, and ability to target diverse disease pathways ensure that small molecules will continue to be a cornerstone of global drug development.
Key Emerging Trends in Small Molecule Drug Development
• Personalized Medicine
Advances in genomics and precision biotechnology are enabling the creation of personalized small molecule therapies tailored to individual genetic profiles, improving treatment outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
• Innovative Drug Delivery Systems
Breakthroughs in delivery technologies—such as nanoparticle carriers, targeted delivery platforms, and controlled-release formulations—are enhancing the efficacy, stability, and safety of small molecule drugs.
• Sustainable & Green Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical companies and CDMOs are increasingly prioritizing sustainable manufacturing, adopting green chemistry, solvent recycling, and low-waste production methods to reduce environmental impact and meet global ESG expectations.
Latest small molecules CDMO News-
Wilmington PharmaTech Partners with Curewell to Expand U.S. Small Molecule API Capacity (Oct 2025)
Lonza Launches Design2Optimize to Accelerate Small Molecule API Development (May 2025)
Flamma Wins 2025 CDMO Leadership Award for Small Molecule API (March 2025)
Shilpa Medicare Launches Hybrid CDMO Model for Small and Large Molecules (March 2025)
Bora Pharmaceuticals Unveils New Small Molecule Facility in Taiwan (Jan 2025)
Download our CDMO News Tracker to stay ahead of every shift in the CDMO landscape.