External Manufacturing (ExM) is the practice of outsourcing specific stages of drug development and production to external partners.
In the biopharmaceutical industry, where 90% of biotechs rely on contract manufacturers to develop therapies (source: Bioplan), it has become a critical function for delivering results.
External Manufacturing involves collaborating with contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs), contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), and other suppliers to handle various aspects of drug manufacturing, quality control, and supply chain management.
- Download our latest report: External Manufacturing Leaders – From Uncertainty to Strategic Resilience
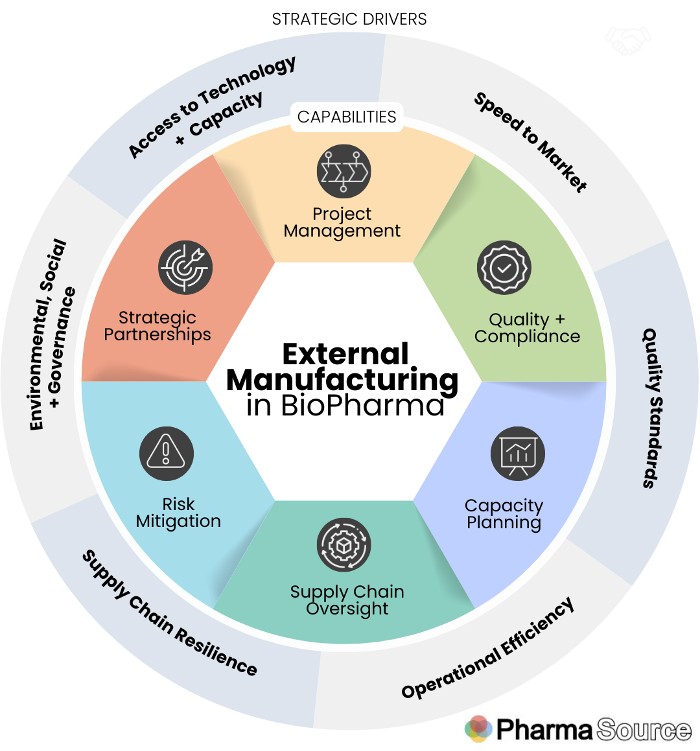
This framework shows both the key drivers for companies choosing to outsource (outer circle) and the capabilities required the manage external manufacturing (inner circle).
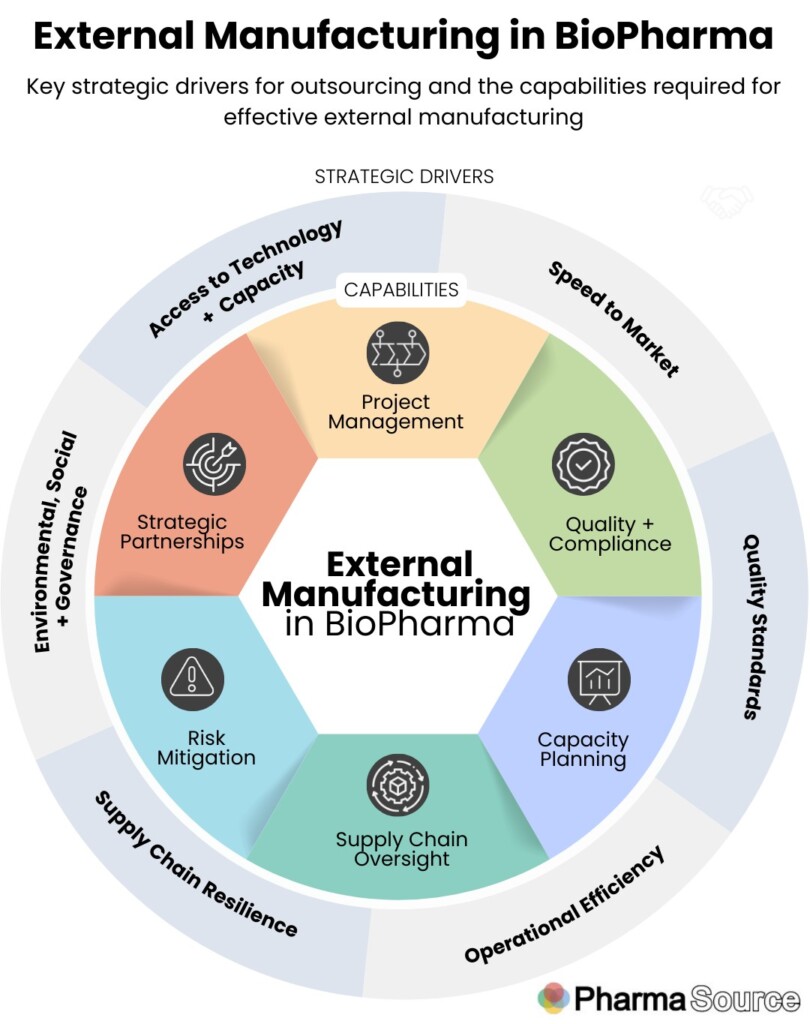
Strategic drivers for external manufacturing
There are a number of drivers for pharma and biotech companies choosing to outsource development and manufacturing to third parties.
- Operational Efficiency
- External manufacturing allows companies to focus on their core competencies while leveraging specialized expertise from external partners. By outsourcing certain functions, such as manufacturing, companies can streamline operations and reduce costs. It enables faster scale-up and capacity expansion, especially for novel therapies like cell and gene therapies, where demand can surge rapidly.
2. Speed to Market
- External Manufacturing accelerates drug development timelines by leveraging external expertise and established processes. Faster tech transfers and efficient collaboration with CMOs enable quicker product launches, benefiting patients and revenue streams.
3. Access to Technology and Capacity
- External manufacturing provides access to cutting-edge manufacturing technologies and facilities that may not be available in-house. This is crucial for producing complex biologics and personalized therapies. Companies can tap into additional production capacity without significant capital investments, ensuring flexibility and responsiveness to market demands.
4. Risk Mitigation:
- Diversifying manufacturing sources reduces the risk of supply disruptions due to unforeseen events (e.g., natural disasters, regulatory issues, or equipment failures). Dual-sourcing allows companies to spread risk across multiple partners, ensuring continuity even if one supplier faces challenges.
5. Quality and Compliance:
- CMOs and CDMOs adhere to stringent quality standards (e.g., cGMP) and regulatory requirements. Collaborating with them ensures consistent product quality and compliance. as they undergo audits and inspections, contributing to overall product safety and efficacy.
6. Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG)
- As the pharmaceutical industry commits to net zero science-based targets and wider ESG goals, outsourcing to the right partners is a key way to make an impact. More than 80% of PSCI member companies’ emissions are in the supply chain, it is imperative that partners are selected based on ESG commitments and worked with to proactively improve their footprint.
External Manufacturing capabilities
External Manufacturing professionals play a multifaceted role, ensuring collaboration, compliance, and efficient production by working with a range of internal stakeholders (including Procurement, Supply Chain, Quality and R&D leads) and with external contract development and manufacturing partners.
To be effective in external manufacturing, there are a number of key areas of responsibility:
Project Management
- Building Strong Connections: External manufacturing professionals act as relationship leads, fostering robust connections with external partners such as contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) and business collaborators. These relationships are critical for effective collaboration, problem-solving, and successful project execution.
- Delivering to a timeline: ExM leaders ensure a regular cadence of communication between the company and external parties to ensure the project timeline is met. They organize meetings, share information, and align goals to drive efficient operations.
Quality and Compliance
- Adherence to cGMP Regulations: External Manufacturing oversees quality control processes, ensuring compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). They manage deviations, product release, and change control to maintain product integrity and regulatory compliance.
- Risk Mitigation: By addressing quality issues promptly, ExM professionals mitigate risks related to product safety, efficacy, and regulatory approvals. Their vigilance ensures that the company’s reputation remains intact.
Capacity Planning
- Resource Allocation: External Manufacturing gathers capacity information from external partners. This data informs resource allocation, production schedules, and capacity utilization. Efficient capacity planning ensures optimal use of manufacturing resources.
- End-to-End Planning: ExM supports robust end-to-end planning, considering factors like production volumes, lead times, and resource availability. They balance supply and demand to meet production goals.
Supply Chain Oversight
- Materials Procurement: External Manufacturing manages raw material procurement, ensuring timely availability for manufacturing. They collaborate with suppliers to maintain a reliable supply chain.
- Logistics and Distribution: From shipping to packaging, ExM oversees logistics. They ensure that products move seamlessly from manufacturing sites to distribution centers or end-users. Effective supply chain management prevents disruptions.
Risk Mitigation
- Addressing Supply Issues: External Manufacturing proactively identifies and resolves supply-related challenges. Whether it’s shortages, delays, or quality concerns, they evaluate cost-benefit scenarios and recommend solutions.
- Regulatory Preparedness: ExM professionals stay informed about industry changes and regulatory updates. By anticipating potential risks, they prepare contingency plans and adapt swiftly to changing requirements.
Strategic Partnerships
- Long-Term Relationships: External Manufacturing will find strategically valuable contract manufacturing partners and forms stable partnerships them. These relationships extend beyond transactional interactions. They contribute to stability, knowledge sharing, and mutual success.
- Business Review Meetings: ExM leaders conduct regular business review meetings with CMOs. These sessions focus on continuous improvement, performance evaluation, and alignment of strategic goals.
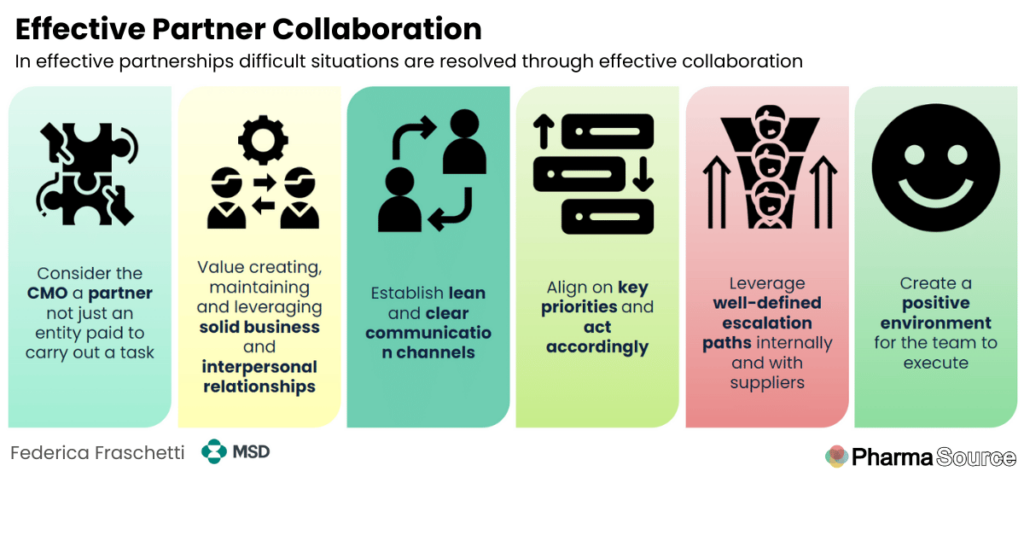
In a recent episode of the PharmaSource podcast, Federica Fraschetti, External Manufacturing lead at MSD explained how to collaborate effectively with contract manufacturing partners.
External Manufacturing Director Job Description
The External Manufacturing Director serves as the organizational leader responsible for developing and executing the global manufacturing strategy through contract manufacturing partnerships.
This senior executive position requires balancing strategic leadership with operational excellence to ensure sustainable growth, quality assurance, and competitive advantage in the marketplace while optimizing costs and maintaining regulatory compliance across multiple regions.
Key Responsibilities
Strategic Leadership and Vision
The director will develop and execute the long-term external manufacturing strategy in alignment with corporate objectives. This includes assessing market conditions, evaluating manufacturing technologies, identifying strategic opportunities, and creating detailed roadmaps for implementation. They must balance cost, quality, and capacity considerations while ensuring the strategy supports business growth targets and maintains competitive advantage.
Team Leadership and Development
Leading a diverse, global team requires building and maintaining high-performing organizations across multiple regions. The director will establish organizational structures, develop talent pipelines, implement succession planning, and create performance management frameworks. They must foster a culture of excellence, accountability, and continuous improvement while ensuring effective communication and collaboration across teams.
Manufacturing Network Optimization
The director will continuously evaluate and optimize the global manufacturing footprint through strategic network design. This involves analyzing capacity requirements, geographical considerations, risk factors, and cost structures to determine the optimal distribution of manufacturing activities. They must also ensure proper redundancy and flexibility within the network to maintain supply chain resilience.
Strategic Partner Management
Establishing and maintaining executive-level relationships with key contract manufacturers is crucial. The director will lead partnership strategies, negotiate major agreements, and ensure alignment of objectives between organizations. This includes regular executive meetings, performance reviews, and strategic planning sessions with manufacturing partners to drive mutual growth and success.
Capital Investment and Financial Management
The role requires directing major capital investments across the manufacturing network, including capacity expansions, technology upgrades, and automation initiatives. The director must develop business cases, perform financial analyses, and prioritize investments based on strategic value and return on investment. They will also manage operating budgets and ensure financial targets are met.
Manage P&L responsibility for external manufacturing operations, develop and manage annual budgets exceeding $100M
Manufacturing Innovation and Technology
Leading manufacturing innovation initiatives involves evaluating new technologies, implementing Industry 4.0 solutions, and driving digital transformation across the manufacturing network. The director must stay current with technological advances, assess their potential impact, and develop implementation strategies that create competitive advantages.
Quality and Regulatory Compliance
Overseeing quality systems and regulatory compliance across all external manufacturing sites is essential. The director will establish quality standards, audit programs, and compliance frameworks while ensuring all manufacturing activities meet regulatory requirements in relevant markets. They must also lead quality improvement initiatives and manage relationships with regulatory bodies.
Risk Management and Business Continuity
Developing comprehensive risk management strategies for the manufacturing network is critical. This includes identifying potential risks, implementing mitigation plans, and ensuring business continuity preparation. The director must regularly assess geopolitical, environmental, financial, and operational risks while maintaining appropriate contingency plans.
New Product Introduction and Technology Transfer
The director will lead the process of transferring new products and technologies to external manufacturing sites. This includes developing transfer protocols, ensuring proper validation, and managing the transition from development to full-scale production. They must coordinate cross-functional teams and ensure smooth implementation while maintaining quality standards.
Continuous Improvement and Operational Excellence
Driving operational excellence requires implementing systematic approaches to continuous improvement across the manufacturing network. The director will establish KPI frameworks, benchmark performance, and lead major improvement initiatives. They must create a culture of operational excellence and ensure best practices are shared across sites.
Required Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Engineering, Manufacturing, Operations, or related field; Master’s degree preferred
- 15+ years of manufacturing experience with at least 8 years in senior leadership roles
- Proven track record of developing and executing manufacturing strategies
- Extensive experience in contract manufacturer selection, negotiation, and relationship management
- Strong understanding of global manufacturing operations, quality systems, and regulatory requirements
- Experience managing budgets and P&L responsibility
- Track record of successful organizational transformation and change management
- Advanced knowledge of manufacturing technologies and Industry 4.0 concepts
Preferred Qualifications
- MBA or Master’s in Engineering/Manufacturing
- Six Sigma Black Belt certification
- Experience in relevant industry sectors
- International work experience
- M&A and post-merger integration experience
- Multi-site manufacturing leadership experience
Leadership Competencies
- Strategic vision and business acumen
- Executive presence and communication skills
- Change management and organizational development
- Global team leadership and talent development
- Financial management and business modeling
- Risk management and mitigation strategies
- Stakeholder management at executive level
- Innovation and digital transformation leadership
Scope of Role
- Team size: 20-50 direct and indirect reports
- Budget responsibility: $100M-500M
- Geographic scope: Global
- Travel requirement: 40-50% international travel
Strategic Responsibilities
- Member of senior leadership team
- Regular board and executive committee presentations
- Key participant in strategic planning process
- Major investment decision-making authority
- Corporate policy development and governance
Executive Benefits Package
- Executive compensation plan
- Annual performance bonus
- Long-term incentive plan
- Stock options/RSUs
- Executive health program
- Retirement planning
- Executive life insurance
- Relocation assistance if required
Reports to: VP of Operations or Chief Operations Officer
Location: Corporate Headquarters with global travel requirements
Employment Type: Full-time, Executive Level
External Manufacturing Leaders events

External Manufacturing Leaders Basel 2025
Exclusive event for senior external manufacturing leaders. 27th August 2025. Basel, Switzerland

External Manufacturing Leaders Boston 2026
Exclusive event for senior external manufacturing leaders. Boston, January 2026

External Manufacturing Leaders Rotterdam 2026
Exclusive event for senior external manufacturing leaders. 26th May 2026 at CDMO Live