
CDMOs vs CROs vs CMOs: Understanding Key Services at Each Stage of Drug Development
In the complex journey of drug development, choosing the right outsourcing partner at each stage is crucial for success.
From early research through to commercial manufacturing, different organizations – Contract Research Organizations (CROs), Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), and Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) – specialize in supporting specific phases of the drug development pipeline.
Understanding when to engage each type of partner can significantly impact your development timeline, costs, and ultimately, your product’s success.
Key Differences Between CDMOs, CROs, and CMOs
What is a CRO?
Contract Research Organizations (CROs) specialize in the research and clinical development phases of drug development. Their expertise lies in managing clinical trials, conducting research studies, and handling regulatory compliance.
CROs provide services such as protocol development, patient recruitment, clinical monitoring, data management, and regulatory submissions. They are crucial partners for companies focusing on drug discovery and clinical development.
What is a CDMO?
Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) offer the most comprehensive service package in the pharmaceutical outsourcing landscape. They provide end-to-end solutions that span from early drug development through to commercial manufacturing.
A CDMO’s services include formulation development, process optimization, analytical method development, scale-up operations, clinical trial material production, and commercial manufacturing. This integrated approach means pharmaceutical companies can work with a single partner throughout their product’s lifecycle, reducing technology transfer risks and potentially accelerating time to market.
What is a CMO?
Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) focus specifically on the manufacturing aspect of pharmaceutical products. Unlike CDMOs, they typically enter the picture once a drug formulation has been finalized and requires large-scale production.
CMOs excel in efficient, compliant manufacturing processes, offering services such as commercial-scale production, packaging, and quality control testing. They are ideal partners for companies that have already developed their products and need reliable, high-quality manufacturing capabilities.
The Drug Development Pipeline: Which Partner When?
Each organization type offers distinct services along the drug development pipeline. as explored in our infographic below.
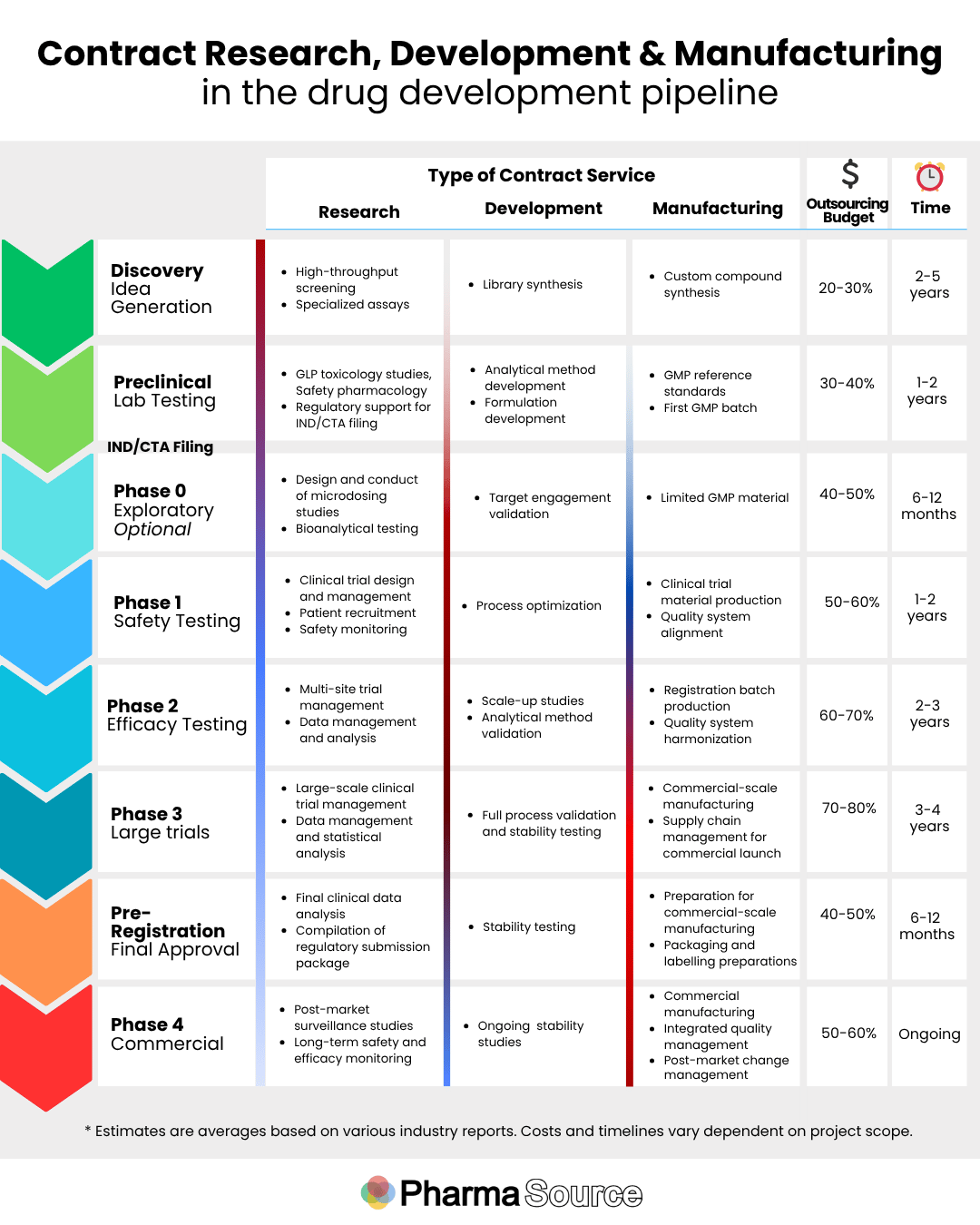
The infographic also includes the services outsourcing partners provide at each stage, industry estimates on the time duration at each stage and the percentage of total budget that is typically allocated to outsourcing at each stage.
The remainder of budget is typically spent on the internal costs such as personnel (including scientific leadership, project management, quality and partner oversight, regulatory affairs and technical operations and infrastructure (including core facilities and office overheads, quality and data management systems).
Mapping services to the drug development timeline
Discovery and Preclinical Stages
During these early stages, outsourcing is at its lowest, with internal costs can represent 80% of budget. Contract Research Organizations (CROs) play a pivotal role at these stages with their specialized research capabilities and laboratory infrastructure support critical activities including:
-
- High-throughput screening and lead identification
-
- Preclinical safety and efficacy studies
-
- GLP toxicology testing
-
- Early analytical method development
-
- Regulatory documentation for IND/CTA filing
CDMOs may also enter the picture at this stage if early process development and manufacturing considerations are crucial to your strategy. They can provide:
-
- Initial process development
-
- Analytical method development
-
- Preliminary formulation studies
-
- Early-stage manufacturing planning
Clinical Development Phases
Phase 1 (Safety Testing)
At this stage, you’ll likely need both CRO and CMO/CDMO support:
CROs manage:
-
- Clinical trial design and protocol development
-
- Patient recruitment and screening
-
- Safety monitoring and reporting
-
- Data management and analysis
CMOs/CDMOs handle:
-
- Clinical trial material production
-
- Initial scale-up activities
-
- Quality system implementation
-
- Stability testing
Phase 2 (Efficacy Testing)
As trials expand, the role of each partner becomes more crucial:
CROs focus on:
-
- Multi-site trial management
-
- Expanded patient recruitment
-
- Efficacy data collection and analysis
-
- Regulatory compliance
CMOs/CDMOs concentrate on:
-
- Process optimization
-
- Larger-scale manufacturing
-
- Quality system harmonization
-
- Supply chain planning
Phase 3 (Large Trials)
At this pivotal stage, all partners play critical roles:
CROs manage:
-
- Large-scale clinical trials
-
- Global site coordination
-
- Comprehensive data analysis
-
- Regulatory submissions
CMOs/CDMOs prepare for commercialization through:
-
- Process validation
-
- Commercial-scale manufacturing preparation
-
- Supply chain optimization
-
- Quality system integration
Commercial Stage
As products move to market, CMOs and CDMOs take center stage:
-
- Commercial-scale manufacturing
-
- Ongoing stability studies
-
- Post-market change management
-
- Supply chain optimization
Cost optimisation strategies: Advice for keeping development costs low
 To avoid running out of cash, it is important to tightly manage outsourcing and internal activities at each stage of development.
To avoid running out of cash, it is important to tightly manage outsourcing and internal activities at each stage of development.
Fabrice Le Garrec shares his advice for cost optimisation in outsourcing:
Standardize Raw Materials and Supply Chain Management
Standardize raw materials and consumables across processes, avoiding specialized or proprietary components. This approach enables competitive sourcing from multiple suppliers, reducing costs and supply chain risks. If possible to use an existing platform, this would normally reduces costs for batches.
Agile Project Management
Implement agile project management methodologies with flexible teams working in focused sprints. Enhance productivity by streamlining documentation requirements and leveraging artificial intelligence for routine tasks.
Enhanced Process Risk Management
Reduce batch failure rates, particularly in biologics manufacturing where failure rates can reach 10%, through improved risk assessment and mitigation strategies. This includes comprehensive monitoring and early intervention protocols.
Operational Excellence Programs
Optimize facility utilization by reducing idle time and streamlining administrative processes. Focus on minimizing time spent on deviation management and other administrative tasks across all departments.
Cross-Functional Team Development
Increase workforce flexibility by training staff in multiple competencies. For example, production operators can be trained to perform quality control testing, reducing overhead costs particularly in early development phases.
Strategic Batch Planning
Carefully evaluate product quantity requirements and optimize batch sizes accordingly. This prevents waste and ensures efficient use of manufacturing resources.
Resource Optimization
Develop evidence-based strategies for reusing appropriate materials, such as filters and cartridges, while maintaining quality standards. This can significantly reduce per-batch costs.
Organizational Efficiency
Streamline management structure at contract manufacturing organizations by consolidating functions and reducing administrative layers.
Facility Utilization
Prioritize multi-purpose manufacturing facilities operating continuously to maximize equipment utilization and minimize the impact of depreciation on batch costs.
Process Innovation
Take a price-driven approach to process development, setting target costs early and engineering processes to meet these targets. This encourages innovative solutions and technological breakthroughs in manufacturing methods.
Ray Sison, Managing Partner, SCxCMC adds the following:
 “Early stage development (discovery through Phase IIa) effort and budget will be heavily dependent on the modality and its complexity. It’s essential to conduct a high-level overview and gap analysis based on available information. Late stage development (Phase IIb/III through launch) will depend on the size of clinical trials among other variables. For larger trials, clinical supplies management is often underestimated.”
“Early stage development (discovery through Phase IIa) effort and budget will be heavily dependent on the modality and its complexity. It’s essential to conduct a high-level overview and gap analysis based on available information. Late stage development (Phase IIb/III through launch) will depend on the size of clinical trials among other variables. For larger trials, clinical supplies management is often underestimated.”
“Timing of spend may be as important as total spend, as many biotech startups are raising capital in parallel with CMC and clinical development plans. Companies can manage cash flow on the CMC side by making fit-for-purpose decisions on drug product development as part of their strategy.”
Making the Decision: Strategic Factors to Consider
Timeline Requirements
Different partners offer varying advantages in terms of development speed:
-
- CROs excel in accelerating clinical development
-
- CMOs can quickly scale up established processes
-
- CDMOs offer efficiency through integrated development and manufacturing
Resource Optimization
Consider how each partner type affects your resource allocation:
-
- CROs reduce the need for internal clinical operations
-
- CMOs eliminate manufacturing infrastructure investments
-
- CDMOs minimize technology transfer requirements
Risk Management
Each partner type offers different risk mitigation strategies:
-
- CROs manage clinical and regulatory risks
-
- CMOs focus on manufacturing compliance
-
- CDMOs provide comprehensive risk management across development and manufacturing
Successful drug development requires selecting the right partners at the right stages. While CROs excel in research and clinical development, CMOs provide manufacturing expertise, and CDMOs offer integrated development and manufacturing solutions. Understanding your needs at each stage of development is crucial for making informed outsourcing decisions that align with your overall development strategy and business objectives.
Connect with the outsourcing ecosystem at CDMO Live 2025 (7-8th May, Rotterdam). Download the full agenda
Drug development timelines and planning
In this video Ray Sison, Managing Partner of SCxCMC, shares integrated drug development timelines and advice for resource planning.
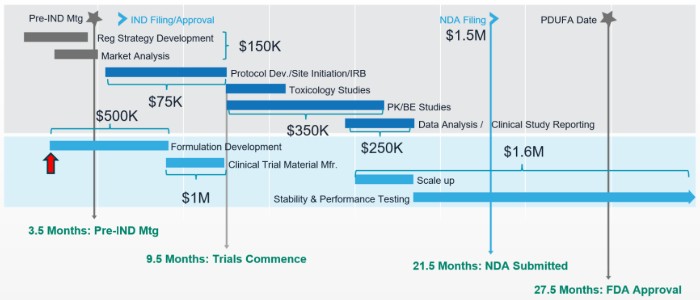
What the short video for an overview of development budgets, hiring timing to spend, and other best practices:
Download the drug development services infographic





