Your guide to choosing the right partner for Pharmaceutical Method Development and Validation.
With an increasing number of drugs entering the market each year, the development of new analytical methods for these drugs is crucial. Once developed, these methods must be validated. The process of analytical method development and validation plays a pivotal role in the discovery, development, and manufacturing of pharmaceuticals.
This guide offers insights into the overall market size and trends, key drivers, opportunities and challenges, leading suppliers in the category, and strategies for enhancing supplier partnerships.
Understanding Analytical Method Development and Validation
The development of a robust analytical method is paramount during the drug discovery process, its release to the market, development, and ultimately, marketing approval. Analytical Method Development and Validation (AMDV) is a multi-step process that involves the design, optimisation, and validation of analytical methods. These methods are used to measure specific drug substances, impurities, and degradation products throughout the drug development and manufacturing process.
The AMDV process includes the selection of the appropriate analytical technique (such as chromatography or spectroscopy), optimisation of sample preparation, establishment of calibration standards, and evaluation of key parameters like accuracy, precision, specificity, and robustness. This comprehensive approach ensures the reliability and consistency of the analytical methods used in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing.
Sub-categories of AMDV:
- Method Development: Creating a new analytical method tailored to your specific needs.
- Method Validation: Rigorously testing and verifying the performance of an existing method.
- Method Transfer: Moving a validated method from one laboratory to another.
- Method Optimisation: Refining an existing method to improve its performance.
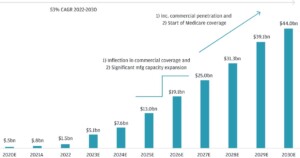
Market size and growth of AMDV
As pharmaceutical companies invest more in new drug development, the demand for accurate and reliable analytical methods rises. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA constantly update their guidelines, necessitating frequent method adaptations and validations.
Market size:
- Expected to reach USD 9.8 billion by 2026, according to Markets and Markets (“Healthcare Analytical Testing Services Market” report)
- Estimated to reach USD 12.39 billion by 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence (“Pharmaceutical Analytical Services Market” report)
- Potential of reaching USD 15.8 billion by 2030, as per PS Market Research (“Pharmaceutical Analytical Testing Outsourcing Market” report)

Growth rate:
- Projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2021 to 2026 (Markets and Markets)
- Expected to expand at a CAGR of 8.41% during 2023-2028 (Mordor Intelligence)
- CAGR of 8.5% predicted from 2022 to 2030 (PS Market Research)
Growth driven factors
The growth is driven by several factors, including increasing pharmaceutical R&D spending, stringent regulatory requirements, development of complex drugs and outsourcing.
- Increasing pharmaceutical R&D spending: As pharma companies invest more in new drug development, the demand for accurate and reliable analytical methods rises.
- Stringent regulatory requirements: Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA constantly update their guidelines, necessitating frequent method adaptations and validations.
- Development of complex drugs: New drug modalities like biologics and gene therapies require specialized analytical techniques, creating new market segments.
- Outsourcing trend: Pharma companies are increasingly outsourcing AMDV services to optimise costs and leverage external expertise.
Market segmentation of AMDV:
The analytical method development and validation (AMDV) market is quite diverse, divided into several key segments catering to different needs and applications. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories:
Service:
- Method Development Services: This segment focuses on developing new analytical methods tailored to specific analytes and matrices. This involves choosing appropriate instruments, optimising parameters, and establishing protocols for sample preparation and analysis.
- Method Validation Services: This segment is concerned with testing and documenting the performance characteristics of established methods. This ensure accuracy, precision, specificity, robustness, and other crucial parameters meet the intended purpose.
Application:
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology: This dominant segment caters to drug development, production, and quality control. Accurate and validated methods are essential for drug safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance.
- Environmental Testing: Monitoring air, water, soil, and other environmental samples for pollutants and contaminants requires specialized methods adapted to complex matrices and specific analytes.
- Food and Beverage: Ensuring food safety and quality control involves analysing for contaminants, toxins, and nutritional content. Methods need to be sensitive, rapid, and robust to handle diverse food matrices.
- Chemical and Materials Science: Characterising chemicals, materials, and their properties often involves unique analytical methods tailored to specific analytes and applications.
- Clinical Diagnostics: Developing and validating laboratory tests for diagnosing diseases and monitoring health conditions is crucial for accurate patient care.
Technology:
- Chromatography-based methods: HPLC, GC, etc., are widely used for separating and analyzing complex mixtures.
- Spectroscopic methods: MS, UV-Vis, FTIR, etc., offer insights into molecular structure and composition.
- Electrochemical methods: Electrochemical sensors and biosensors provide rapid and sensitive analysis for specific analytes.
- Digital and Software Solutions: Automation, data acquisition, and analysis software play a vital role in efficient and reliable AMDV.
Market trends
There are a number of key Market trends of AMDV to consider
- Automation and miniaturisation: Increased adoption of automated and miniaturised instruments improves efficiency and reduces sample size.
- High-throughput screening (HTS): HTS technologies accelerate drug discovery by analysing large libraries of compounds simultaneously.
- Data integration and analytics: Integration of analytical data with other research data provides deeper insights into drug properties and performance.
- Digitalisation and cloud-based platforms: Cloud-based platforms offer accessible data storage, analysis, and collaboration tools.
Benefits of Partnering with an AMDV Supplier:
- Expertise and experience: Access to a team of skilled scientists with deep knowledge of various analytical techniques and regulatory requirements.
- Efficiency and speed: Get your methods developed and validated faster, allowing for quicker drug development and market entry.
- Cost optimisation: Leverage the supplier’s expertise to design and implement cost-effective methods, reducing internal resource dedication.
- Compliance assurance: Gain confidence that your methods meet regulatory standards, minimizing the risk of delays or rejections.
Challenges
- Rising labour costs: Skilled scientists are in high demand, leading to increasing labour costs for AMDV services.
- Regulatory complexity: Navigating ever-changing regulatory requirements can be complex and expensive.
- Data integrity and security: Ensuring data integrity and security throughout the analytical process is crucial.
- Competition and pricing pressure: Intense competition can lead to price pressure and reduced profit margins
Opportunities
- Automation and miniaturisation: Increased adoption of automated and miniaturised instruments improves efficiency and reduces sample size.
- High-throughput screening (HTS): HTS technologies accelerate drug discovery by analysing large libraries of compounds simultaneously.
- Data integration and analytics: Integration of analytical data with other research data provides deeper insights into drug properties and performance.
- Digitalisation and cloud-based platforms: Cloud-based platforms offer accessible data storage, analysis, and collaboration tools.
Key AMDV partners
The AMDV market is fragmented, with a mix of large multinationals, specialized CROs, and smaller regional players. Key players include:
- Charles River Laboratories
- Eurofins Scientific
- SGS Life Sciences
- WuXi AppTec
- Covance
- Alcami Corporation
- Syneos Health
How to find the right AMDV partner
When it comes to choosing the right AMDV supplier, it is essential to consider several factors to ensure that you reap the benefits while minimising potential challenges. Here are some of the key factors to consider:
- Technical expertise: Look for a supplier with experience in your specific analytical needs and familiarity with relevant regulatory requirements.
- Track record: Ask for case studies and references to assess the supplier’s success in similar projects.
- Communication and collaboration: Choose a partner who readily communicates, understands your goals, and can tailor solutions to your specific needs.
- Quality management system: Ensure the supplier has a robust quality management system in place to guarantee data integrity and compliance.
- Cost and pricing structure: Compare pricing models and ensure transparency in invoicing and project timelines.
By following these guidelines, you can find a reliable supplier that meets your specific needs and provides the most value for your money.