The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a major transformation as it embraces the digital revolution. The term Pharma 4.0 refers to the application of Industry 4.0 principles and technologies to the specific context and challenges of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Pharma 4.0 aims to improve product quality, patient safety, operational efficiency, and innovation, while simplifying compliance and regulatory oversight. However, achieving this vision requires a shift in mindset and a holistic approach that involves business, IT, and manufacturing stakeholders throughout the drug product lifecycle.
What is Pharma 4.0?
Pharma 4.0 is a term that describes the application of Industry 4.0 principles and technologies to the pharmaceutical industry. Industry 4.0 is the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of physical and digital systems, the use of big data and analytics, the adoption of cloud computing and the internet of things, and the emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies enable smart, connected, and autonomous manufacturing processes that can optimize performance, quality, and efficiency.

Pharma 4.0 is not just a technological change, but also a cultural and organizational one. It requires a shift in mindset from a traditional, linear, and siloed approach to a more agile, collaborative, and holistic one. It also involves a human-centric approach that empowers the workforce and enhances their skills and capabilities. Pharma 4.0 aims to create a seamless and transparent flow of information and knowledge across the entire drug product lifecycle, from research and development to manufacturing and distribution.
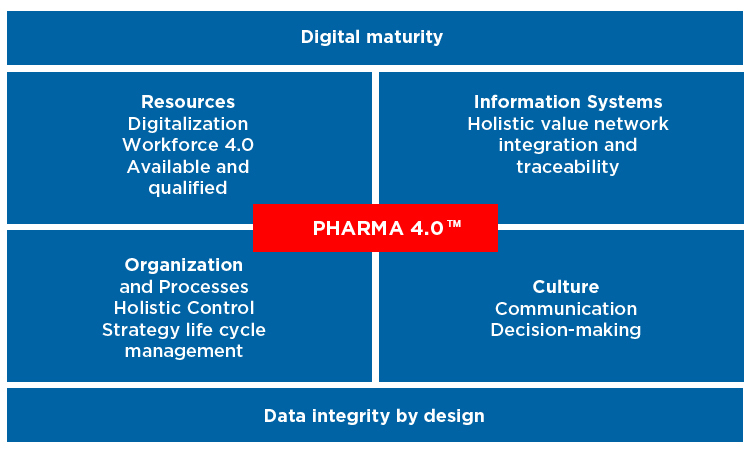
The term Pharma 4.0 was trademarked by the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineers (ISPE) in 2017, as part of their initiative to provide guidance and best practices for the pharmaceutical industry to accelerate its digital transformation. The ISPE developed a framework for Pharma 4.0 that outlines the target components and enablers of the new operating model, as well as the maturity levels and the roadmap for implementation. The framework is based on four key principles: interoperability, information transparency, technical assistance, and decentralized decisions.
According to the ISPE, Pharma 4.0 “is not a destination, but a journey”. It is a continuous process of improvement and innovation that leverages the opportunities and challenges of the digital era. Pharma 4.0 is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but a tailored and flexible approach that adapts to the specific needs and goals of each organization. Pharma 4.0 is not a threat, but an opportunity. It is a way to enhance product quality, patient safety, operational efficiency, and innovation, while simplifying compliance and regulatory oversight.
What are the benefits of industry 4.0 to the pharmaceutical industry?
Pharma 4.0 offers a number of benefits for the pharmaceutical industry, both in terms of business outcomes and social impact. Some of the main benefits are:
- Improved product quality and patient safety: Pharma 4.0 enables real-time monitoring and control of the critical quality attributes and parameters of the drug products, as well as the traceability and integrity of the data throughout the supply chain. This reduces the risk of errors, deviations, and recalls, and ensures the consistency and reliability of the products. Moreover, Pharma 4.0 allows for more personalized and targeted therapies, as well as faster and more efficient clinical trials, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
- Enhanced operational efficiency and productivity: Pharma 4.0 leverages the power of data and analytics to optimize the performance and utilization of the assets, resources, and processes involved in drug production. This results in lower costs, higher yields, shorter lead times, and less waste. Furthermore, Pharma 4.0 enables more flexible and agile manufacturing, as well as the integration and collaboration of the different functions and stakeholders across the value chain, improving the responsiveness and adaptability of the industry to the changing market demands and customer needs.
- Increased innovation and competitiveness: Pharma 4.0 fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, as well as the adoption of new technologies and business models. This allows the industry to explore new opportunities and solutions, as well as to enhance its capabilities and competencies. Pharma 4.0 also helps the industry to overcome the challenges and barriers of the regulatory environment, by simplifying and streamlining the compliance and validation processes, and by facilitating the communication and cooperation with the authorities and the regulators.
- Simplified compliance and regulatory oversight: Pharma 4.0 ensures the compliance and regulatory oversight of the pharmaceutical industry, by providing a transparent and reliable digital record of the entire drug product lifecycle, from the raw materials to the final product. This enables the industry to demonstrate the quality and safety of its products, as well as to comply with the standards and regulations of the different markets and regions. Moreover, Pharma 4.0 enables a more proactive and risk-based approach to compliance and validation, as well as a more collaborative and constructive relationship with the regulators and the auditors.
- Sustainability: These benefits are not only beneficial for the pharmaceutical industry, but also for the society and the environment. By improving the quality and safety of the drug products, Pharma 4.0 contributes to the health and well-being of the patients and the consumers. By enhancing the operational efficiency and productivity of the drug production, Pharma 4.0 reduces the environmental impact and the carbon footprint of the industry.
How do you effectively implement Pharma 4.0 technologies?
Implementing Pharma 4.0 technologies is not a simple or straightforward task. It requires a strategic and systematic approach that considers the specific needs and goals of each organization, as well as the challenges and opportunities of the digital era.
Here are some key steps or strategies for implementing Pharma 4.0 technologies effectively:
1. Assessing the current state and maturity level of the organization
The first step is to understand the current situation and the readiness of the organization for the digital transformation. This involves conducting a gap analysis and a maturity assessment, using tools such as the ISPE Pharma 4.0 Maturity Model or the GAMP 5 Maturity Model. The assessment should cover the following aspects: business objectives, IT infrastructure, manufacturing processes, data management, quality systems, regulatory compliance, organizational culture, and workforce skills.
2. Identifying the gaps and opportunities for improvement
The next step is to identify the areas where the organization can improve its performance, quality, efficiency, and innovation, by leveraging the potential of the digital technologies. This involves defining the pain points and the root causes, as well as the desired outcomes and the key performance indicators. The identification should also consider the customer needs and expectations, the market trends and demands, and the regulatory requirements and standards, and prioritise the most impactful solutions, based onthe return on investment.
3. Developing a roadmap and a business case for the transformation
The third step is to develop a roadmap and a business case for the digital transformation, based on the gap analysis and the opportunity identification. The roadmap should outline the vision and the mission, the goals and the objectives, the scope and the boundaries, the timeline and the milestones, the resources and the budget, and the roles and the responsibilities of the transformation. The business case should justify the need and the value of the transformation, as well as the costs and the benefits, the risks and the mitigations, and the assumptions and the dependencies of the transformation.
4. Engaging and empowering the stakeholders and the workforce
The fourth step is to engage and empower the stakeholders and the workforce, who are the key enablers and the beneficiaries of the digital transformation. This involves creating and fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement and communicating with the internal and external stakeholders, such as the management, the employees, the customers, the suppliers, the partners, and the regulators, to ensure their awareness, involvement, support, and satisfaction.
5. Deploying and integrating the technologies with the existing systems and processes
The fifth step is to deploy and integrate the digital technologies with the existing systems and processes, following the roadmap and the business case. This involves selecting and implementing the appropriate technologies, such as sensors, cloud, IoT, AI, ML, etc., that can address the specific needs and goals of the organization. This also involves integrating, testing and harmonizing the technologies with the existing systems and processes, such as ERP, MES, LIMS, etc., to ensure the interoperability and the information transparency.
6. Monitoring and evaluating the results and the return on investment
The sixth and final step is to monitor and evaluate the results and the return on investment of the digital transformation, using the key performance indicators and the feedback mechanisms. This involves measuring and analysing the performance, quality, efficiency, and innovation of the organization, as well as the satisfaction and loyalty of the customers, before and after the transformation. This also involves comparing and benchmarking the results and the return on investment with the expected outcomes and the value proposition, as well as with the best practices and the industry standards.
These steps or strategies are not sequential or linear, but rather iterative and cyclical. They should be repeated and refined as the organization progresses and matures in its digital journey and adapted to the specific context and challenges of each organization.
Steps towards digital maturity
One of the enablers of the Pharma 4.0 operating model is digital maturity. There are six stages in digital maturity which will help companies transition to Pharma 4.0.
Step 1: Computerization
The first level of maturity is the automation of simple manual processes with the introduction of digital technology. The goal is to find repetitive tasks that would be better performed by the computers that form the basis of the digital infrastructure. For example, using barcode scanners to track inventory, or using electronic batch records to document production data.
Step 2: Connectivity
In the second stage of Pharma 4.0 maturity, the equipment and devices for drug production are connected to the network. It enables data collection and communication between devices. It also creates a basis for connecting IT infrastructure, business and production. For example, using sensors to monitor temperature, pressure, or pH, or using cloud services to store and access data.
Step 3: Visibility
At this point, you will see significant progress in your drug production. A connected ecosystem of people, machines and processes creates meaningful digital output that enables intelligent and informed decisions in real-time. For example, using dashboards to visualize production performance, or using analytics to identify trends and patterns.
Step 4: Transparency
As more data is collected, Pharma 4.0 enables a new type of transparency never before seen in manufacturing. Everyone in the supply chain has access to the same data, enabling better communication and collaboration. These advanced analytics help uncover opportunities for improvement that were previously anonymous and invisible. For example, using blockchain to ensure data integrity and traceability, or using artificial intelligence to optimize processes and resources.
Step 5: Predictability
Detailed production data allows manufacturers to solve problems before they happen. The predictability and precaution lead to less downtime, fewer recalls, and better quality. For example, using machine learning to predict failures and maintenance needs, or using simulation to test and validate changes and scenarios.
Step 6: Adaptability
In the final stage of maturity, Pharma 4.0 manufacturing processes are adjusted in real-time. This is also possible through continuous data collection and the use of advanced analytics. In addition, the systems automate themselves to prevent problems and they in turn initiate the corresponding actions without human intervention.