An overview of the Intermediates manufacturing category for pharmaceutical procurement teams. This guide provides you with the overall market size and trends, key drivers, opportunities and challenges, contract manufacturers in the category and advice on how to improve strategic supplier partnerships.
Definition
Intermediates refer to chemical compounds that are used as building blocks or precursor materials in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or finished pharmaceutical products.
These intermediates play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry by enabling the efficient and cost-effective production of drugs.
Pharmaceutical intermediates can include various organic and inorganic compounds, such as reagents, catalysts, chiral compounds, and other functional groups, which are utilised at different stages of the drug manufacturing process.
Pharmaceutical intermediates serve as a critical link between the discovery of new drug candidates and the commercial production of pharmaceutical products. They allow for the synthesis of complex molecules and provide the necessary chemical transformations to convert raw materials into active drugs.
Pharmaceutical intermediates contribute to enhancing drug efficacy, stability, and bioavailability, thereby ensuring the quality and effectiveness of medications. These intermediates also play a vital role in achieving regulatory compliance by meeting the stringent standards set by regulatory authorities.
Market Size and Trends
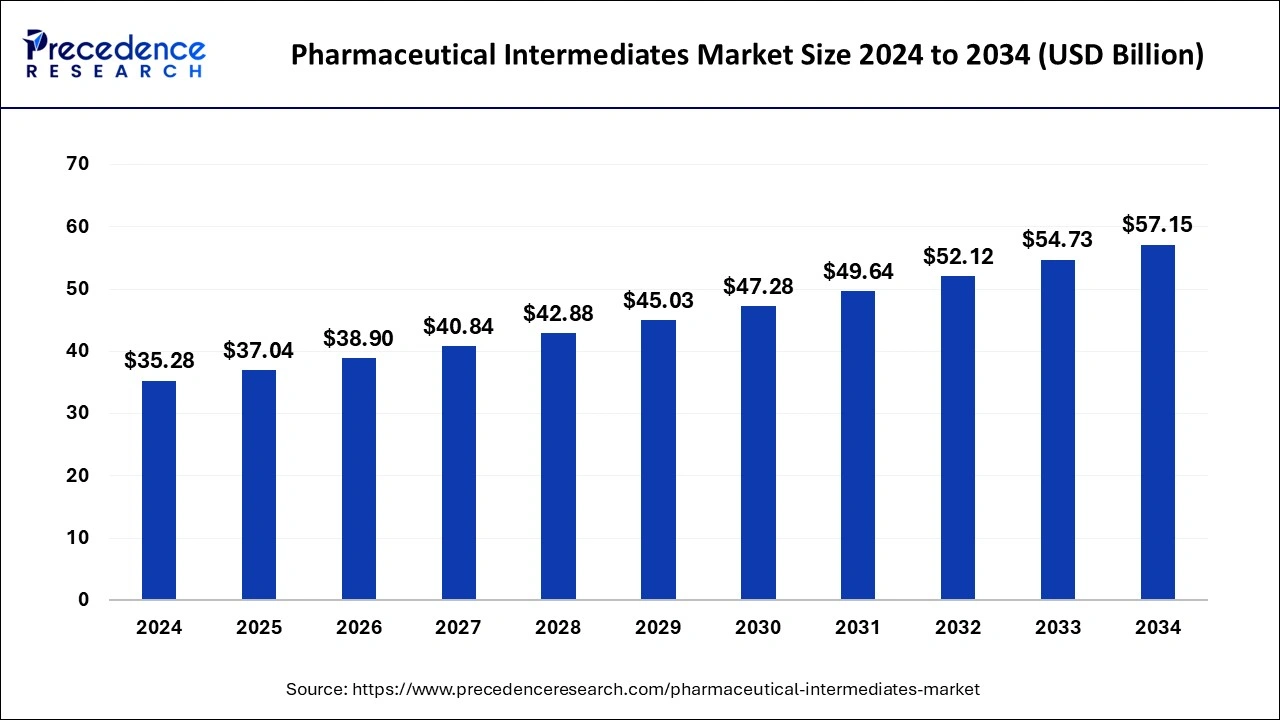
The global pharmaceutical intermediate market size is accounted at USD 37.04 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to hit around USD 57.15 billion by 2034, representing a CAGR of 4.94% from 2025 to 2034. (Source- Precedence Research)
This growth can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing demand for generic drugs, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the expansion of pharmaceutical manufacturing activities in emerging markets.
The market growth is also driven by advancements in drug development and the need for efficient and cost-effective production processes. Pharmaceutical intermediates play a crucial role in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and the manufacturing of finished pharmaceutical products. These intermediates serve as building blocks and precursor materials, enabling the transformation of raw materials into complex molecules required for drug production.
Strengths
Weaknesses
Strengths
Robust Manufacturing Infrastructure: The pharmaceutical intermediate market benefits from well-established manufacturing facilities equipped with advanced technologies and efficient production processes. This infrastructure enables the production of high-quality intermediates in large quantities.
Strong Research and Development Capabilities: The industry’s focus on innovation and continuous improvement drives the development of novel synthesis routes and manufacturing processes. The ability to create and optimize efficient and cost-effective intermediate production methods is a significant strength
Regulatory Compliance: Pharmaceutical intermediates manufacturers are experienced in navigating complex regulatory frameworks and ensuring compliance with stringent quality and safety standards. Adhering to regulatory requirements enhances the credibility and trustworthiness of manufacturers.
Customization and Flexibility: Manufacturers often offer customized synthesis services to meet specific customer requirements. This ability to tailor intermediates to unique specifications provides a competitive edge and fosters strong customer relationships.
Weaknesses
Intellectual Property Risks: Developing proprietary synthesis routes and protecting intellectual property can be challenging. There is a risk of unauthorized duplication or infringement, which can undermine the competitive advantage of manufacturers.
Quality Control Challenges: Maintaining consistent quality across different batches of intermediates is a complex task. Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency, purity, and stability requires robust quality control systems and analytical testing protocols.
Dependence on Raw Materials: The availability and cost of raw materials can impact the production and profitability of pharmaceutical intermediates. Manufacturers need to manage the supply chain effectively to mitigate the risks associated with raw material sourcing.
Opportunities
Threats
Opportunities
Growing Pharmaceutical Industry: The global pharmaceutical industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by factors such as an ageing population, increased healthcare expenditure, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases. This growth presents opportunities for the pharmaceutical intermediate market to expand its customer base and meet the growing demand for APIs and finished pharmaceutical products.
Increasing Outsourcing of Manufacturing: Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly outsourcing intermediate manufacturing to contract manufacturers to leverage cost advantages, access specialised expertise, and enhance operational flexibility. This trend creates opportunities for contract manufacturers to expand their customer base and develop long-term partnerships.
Emerging Markets: Emerging markets, particularly in Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East, offer significant growth potential for pharmaceutical intermediates. The expanding pharmaceutical industries in these regions, coupled with favourable government initiatives and rising healthcare investments, present opportunities for market expansion and collaboration.
Threats
Regulatory Challenges: Evolving regulatory requirements and increasing scrutiny from regulatory authorities pose challenges for manufacturers. Compliance with complex regulations, including GMP standards, can be resource-intensive and impact production timelines.
Competitive Landscape: The pharmaceutical intermediate market is highly competitive, with several established players and new entrants. Intense competition can lead to price pressures and reduced profit margins, especially when combined with factors such as raw material price fluctuations and market volatility.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters, trade conflicts, or pandemics, can impact the availability of raw materials and hinder production. Manufacturers need to implement effective supply chain management strategies to mitigate these risks.
Technological Advancements: While technological advancements provide opportunities, they also pose threats. Rapidly evolving technologies can render existing manufacturing processes obsolete, requiring manufacturers to continually invest in research and development to stay competitive.
APIs vs. Intermediates: Key Differences
How to create better partnerships with Intermediate Contract Manufacturers
Partnering with intermediate contract manufacturers can provide numerous benefits, including cost savings, flexibility, and access to specialised expertise.
However, effective collaboration and management of such partnerships are essential to ensure seamless operations, maintain quality standards, and manage costs, especially during periods of high inflation.
The following steps are recommended for pharmaceutical procurement teams on how to partner better with intermediate contract manufacturers while managing costs without compromising quality.
1. Establish Clear Communication Channels
Clear and open communication is key to successful partnerships with intermediate contract manufacturers. Establishing effective communication channels and maintaining regular contact can help align expectations, address concerns promptly, and ensure a smooth flow of information. Regular meetings, both virtual and in-person when possible, can facilitate proactive collaboration, risk management, and decision-making.
2. Define Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defining roles and responsibilities is crucial to avoid confusion and ensure accountability. Establishing a detailed scope of work and a well-defined agreement that outlines the respective responsibilities of the pharmaceutical company and the contract manufacturer will help manage expectations and streamline operations.
Regularly review and update these agreements to accommodate changing needs and evolving market dynamics.
3. Foster Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing between the pharmaceutical company and the contract manufacturer. This can include joint problem-solving sessions, cross-functional teams, and technology transfer initiatives. By sharing expertise, insights, and best practices, both parties can optimize processes, improve efficiency, and enhance the quality of the intermediates.
4. Emphasise Quality Management
Maintaining quality standards is of paramount importance. Establish a robust quality management system that aligns with regulatory requirements and industry best practices. Conduct regular audits, both internal and external, to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Implement a thorough supplier qualification process and regularly monitor the performance of the contract manufacturer to maintain consistent quality throughout the partnership.
5. Cost Management Strategies
During times of high inflation and rising costs, managing expenses while upholding quality becomes crucial. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Long-Term Contracts: Negotiate long-term contracts with contract manufacturers to secure pricing stability and avoid sudden cost fluctuations. This provides both parties with visibility and enables better financial planning.
- Supplier Consolidation: Consolidate your contracts with a smaller number of contract manufacturers to leverage volume discounts and streamline procurement processes. This can result in cost savings and improved efficiency.
- Value Engineering: Collaborate with contract manufacturers to identify opportunities for value engineering and cost optimization. Analyze the manufacturing process, identify inefficiencies, and explore alternative materials or processes that can reduce costs without compromising quality.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Optimize your supply chain by reducing lead times, improving inventory management, and implementing just-in-time practices. This can help minimize holding costs and inventory write-offs.
- Continuous Improvement: Implement a culture of continuous improvement and cost-consciousness. Encourage contract manufacturers to suggest cost-saving initiatives, foster process optimization, and reward efficiency gains.
6. Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Identify potential risks in the partnership and develop contingency plans to mitigate their impact. This can include alternative sourcing options, backup suppliers, and crisis management strategies. Regularly assess and update risk profiles to stay proactive in managing potential disruptions.
7. Performance Measurement and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establish performance measurement metrics and KPIs to monitor the contract manufacturer’s performance. Regularly evaluate their adherence to quality standards, delivery timelines, responsiveness, and cost management. Engage in constructive dialogue to address any performance gaps and identify opportunities for improvement.
8. Long-Term Relationship Building
Building long-term relationships with contract manufacturers is beneficial for both parties. Invest in fostering trust, open communication, and mutual understanding. Encourage collaboration beyond the transactional level and strive for a strategic partnership. Regularly review and evaluate the contract manufacturer’s performance and provide feedback for continuous improvement. Celebrate successes and recognize the contributions of the contract manufacturer to reinforce the partnership.
9. Embrace Innovation and Technology
Stay abreast of the latest advancements in pharmaceutical manufacturing and encourage contract manufacturers to adopt innovative technologies and processes. Embracing automation, digitalization, and data analytics can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Collaborate with contract manufacturers to explore opportunities for process optimization and innovation that can drive mutual benefits.
10. Continuous Evaluation and Benchmarking
Regularly evaluate the performance of the contract manufacturer against industry benchmarks and best practices. Benchmarking allows you to identify areas of improvement, compare performance against industry standards, and drive excellence. Engage in open discussions with contract manufacturers to align goals, implement feedback mechanisms, and drive continuous improvement.
Partnering with intermediate contract manufacturers in the pharmaceutical industry offers numerous benefits, but effective management is crucial. By establishing clear communication channels, defining roles and responsibilities, fostering collaboration, emphasizing quality management, implementing cost management strategies, and building long-term relationships, pharmaceutical procurement teams can enhance their partnerships with contract manufacturers while managing costs and maintaining quality. Embrace innovation, continuously evaluate performance, and engage in open dialogue to drive mutual success and achieve strategic objectives.
FAQs-
1. What are pharmaceutical intermediates?
Pharmaceutical intermediates are chemical compounds used as building blocks during the multi-step synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or finished drug products.
2. Why are intermediates important in drug development?
They enable complex chemical transformations, support molecule stability, enhance bioavailability, and ensure the final drug meets required quality and regulatory standards.
3. What factors are driving growth in the pharmaceutical intermediates market?
Growth is driven by rising demand for generics, increasing chronic disease prevalence, expansion of manufacturing in emerging markets, and the need for efficient, cost-effective synthesis processes.
4. What challenges do manufacturers face when producing intermediates?
Challenges include maintaining quality consistency, managing raw material supply, protecting intellectual property, and meeting evolving regulatory requirements.
5. Why are pharmaceutical companies outsourcing intermediate manufacturing?
Companies outsource to access specialised synthesis expertise, reduce costs, improve flexibility, and scale production efficiently while focusing on core R&D.
6. What should procurement teams consider when partnering with intermediate manufacturers?
They should ensure clear communication, strong quality systems, well-defined roles, cost-management strategies, robust risk mitigation, and long-term relationship building.
Download our CDMO News Tracker to stay ahead of every shift in the CDMO landscape.
Download our CDMO News Tracker to stay ahead of every shift in the CDMO landscape.









